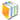polar coordinates

[计] 极坐标
Polar \Po"lar\, a. [Cf. F. polaire. See {Pole} of the earth.]
1. Of or pertaining to one of the poles of the earth, or of a
sphere; situated near, or proceeding from, one of the
poles; as, polar regions; polar seas; polar winds.
2. Of or pertaining to the magnetic pole, or to the point to
which the magnetic needle is directed.
3. (Geom.) Pertaining to, reckoned from, or having a common
radiating point; as, polar co["o]rdinates.
{Polar axis}, that axis of an astronomical instrument, as an
equatorial, which is parallel to the earths axis.
{Polar bear} (Zo["o]l.), a large bear ({Ursus maritimus} syn.
{Thalarctos maritimus}) inhabiting the arctic regions. It
sometimes measures nearly nine feet in length and weighs
1,600 pounds. It is partially amphibious, very powerful,
and the most carnivorous of all the bears. The fur is
white, tinged with yellow. Called also {White bear}. See
{Bear}.
{Polar body}, {Polar cell}, or {Polar globule} (Biol.), a
minute cell which separates by karyokinesis from the ovum
during its maturation. In the maturation of ordinary ova
two polar bodies are formed, but in parthogenetic ova only
one. The first polar body formed is usually larger than
the second one, and often divides into two after its
separation from the ovum. Each of the polar bodies removes
maternal chromatin from the ovum to make room for the
chromatin of the fertilizing spermatozo["o]n; but their
functions are not fully understood.
{Polar circles} (Astron. & Geog.), two circles, each at a
distance from a pole of the earth equal to the obliquity
of the ecliptic, or about 23[deg] 28', the northern called
the arctic circle, and the southern the antarctic circle.
{Polar clock}, a tube, containing a polarizing apparatus,
turning on an axis parallel to that of the earth, and
indicating the hour of the day on an hour circle, by being
turned toward the plane of maximum polarization of the
light of the sky, which is always 90[deg] from the sun.
{Polar co["o]rdinates}. See under 3d {Co["o]rdinate}.
{Polar dial}, a dial whose plane is parallel to a great
circle passing through the poles of the earth. --Math.
Dict.
{Polar distance}, the angular distance of any point on a
sphere from one of its poles, particularly of a heavenly
body from the north pole of the heavens.
{Polar equation of a line} or {Polar equation of a surface},
an equation which expresses the relation between the polar
co["o]rdinates of every point of the line or surface.
{Polar forces} (Physics), forces that are developed and act
in pairs, with opposite tendencies or properties in the
two elements, as magnetism, electricity, etc.
{Polar hare} (Zo["o]l.), a large hare of Arctic America
({Lepus arcticus}), which turns pure white in winter. It
is probably a variety of the common European hare ({Lepus
timidus}).
{Polar lights}, the aurora borealis or australis.
{Polar opposition}, or {Polaric opposition} or {Polar
contrast} or {Polaric contrast} (Logic), an opposition or
contrast made by the existence of two opposite conceptions
which are the extremes in a species, as white and black in
colors; hence, as great an opposition or contrast as
possible.
{Polar projection}. See under {Projection}.
{Polar spherical triangle} (Spherics), a spherical triangle
whose three angular points are poles of the sides of a
given triangle. See 4th {Pole}, 2.
{Polar whale} (Zo["o]l.), the right whale, or bowhead. See
{Whale}.
Coordinate \Co*["o]r"di*nate\, n.
1. A thing of the same rank with another thing; one two or
more persons or things of equal rank, authority, or
importance.
It has neither co["o]rdinate nor analogon; it is
absolutely one. --Coleridge.
2. pl. (Math.) Lines, or other elements of reference, by
means of which the position of any point, as of a curve,
is defined with respect to certain fixed lines, or planes,
called co["o]rdinate axes and co["o]rdinate planes. See
{Abscissa}.
Note: Co["o]rdinates are of several kinds, consisting in some
of the different cases, of the following elements,
namely:
(a) (Geom. of Two Dimensions) The abscissa and ordinate of
any point, taken together; as the abscissa PY and
ordinate PX of the point P (Fig. 2, referred to the
co["o]rdinate axes AY and AX.
(b) Any radius vector PA (Fig. 1), together with its angle
of inclination to a fixed line, APX, by which any
point A in the same plane is referred to that fixed
line, and a fixed point in it, called the pole, P.
(c) (Geom. of Three Dimensions) Any three lines, or
distances, PB, PC, PD (Fig. 3), taken parallel to
three co["o]rdinate axes, AX, AY, AZ, and measured
from the corresponding co["o]rdinate fixed planes,
YAZ, XAZ, XAY, to any point in space, P, whose
position is thereby determined with respect to these
planes and axes.
(d) A radius vector, the angle which it makes with a fixed
plane, and the angle which its projection on the plane
makes with a fixed line line in the plane, by which
means any point in space at the free extremity of the
radius vector is referred to that fixed plane and
fixed line, and a fixed point in that line, the pole
of the radius vector.
{Cartesian co["o]rdinates}. See under {Cartesian}.
{Geographical co["o]rdinates}, the latitude and longitude of
a place, by which its relative situation on the globe is
known. The height of the above the sea level constitutes a
third co["o]rdinate.
{Polar co["o]rdinates}, co["o]rdinates made up of a radius
vector and its angle of inclination to another line, or a
line and plane; as those defined in
(b) and
(d) above.
{Rectangular co["o]rdinates}, co["o]rdinates the axes of
which intersect at right angles.
{Rectilinear co["o]rdinates}, co["o]rdinates made up of right
lines. Those defined in
(a) and
(c) above are called also {Cartesian co["o]rdinates}.
{Trigonometrical co["o]rdinates} or {Spherical
co["o]rdinates}, elements of reference, by means of which the
position of a point on the surface of a sphere may be
determined with respect to two great circles of the
sphere.
{Trilinear co["o]rdinates}, co["o]rdinates of a point in a
plane, consisting of the three ratios which the three
distances of the point from three fixed lines have one to
another.
1. Of or pertaining to one of the poles of the earth, or of a
sphere; situated near, or proceeding from, one of the
poles; as, polar regions; polar seas; polar winds.
2. Of or pertaining to the magnetic pole, or to the point to
which the magnetic needle is directed.
3. (Geom.) Pertaining to, reckoned from, or having a common
radiating point; as, polar co["o]rdinates.
{Polar axis}, that axis of an astronomical instrument, as an
equatorial, which is parallel to the earths axis.
{Polar bear} (Zo["o]l.), a large bear ({Ursus maritimus} syn.
{Thalarctos maritimus}) inhabiting the arctic regions. It
sometimes measures nearly nine feet in length and weighs
1,600 pounds. It is partially amphibious, very powerful,
and the most carnivorous of all the bears. The fur is
white, tinged with yellow. Called also {White bear}. See
{Bear}.
{Polar body}, {Polar cell}, or {Polar globule} (Biol.), a
minute cell which separates by karyokinesis from the ovum
during its maturation. In the maturation of ordinary ova
two polar bodies are formed, but in parthogenetic ova only
one. The first polar body formed is usually larger than
the second one, and often divides into two after its
separation from the ovum. Each of the polar bodies removes
maternal chromatin from the ovum to make room for the
chromatin of the fertilizing spermatozo["o]n; but their
functions are not fully understood.
{Polar circles} (Astron. & Geog.), two circles, each at a
distance from a pole of the earth equal to the obliquity
of the ecliptic, or about 23[deg] 28', the northern called
the arctic circle, and the southern the antarctic circle.
{Polar clock}, a tube, containing a polarizing apparatus,
turning on an axis parallel to that of the earth, and
indicating the hour of the day on an hour circle, by being
turned toward the plane of maximum polarization of the
light of the sky, which is always 90[deg] from the sun.
{Polar co["o]rdinates}. See under 3d {Co["o]rdinate}.
{Polar dial}, a dial whose plane is parallel to a great
circle passing through the poles of the earth. --Math.
Dict.
{Polar distance}, the angular distance of any point on a
sphere from one of its poles, particularly of a heavenly
body from the north pole of the heavens.
{Polar equation of a line} or {Polar equation of a surface},
an equation which expresses the relation between the polar
co["o]rdinates of every point of the line or surface.
{Polar forces} (Physics), forces that are developed and act
in pairs, with opposite tendencies or properties in the
two elements, as magnetism, electricity, etc.
{Polar hare} (Zo["o]l.), a large hare of Arctic America
({Lepus arcticus}), which turns pure white in winter. It
is probably a variety of the common European hare ({Lepus
timidus}).
{Polar lights}, the aurora borealis or australis.
{Polar opposition}, or {Polaric opposition} or {Polar
contrast} or {Polaric contrast} (Logic), an opposition or
contrast made by the existence of two opposite conceptions
which are the extremes in a species, as white and black in
colors; hence, as great an opposition or contrast as
possible.
{Polar projection}. See under {Projection}.
{Polar spherical triangle} (Spherics), a spherical triangle
whose three angular points are poles of the sides of a
given triangle. See 4th {Pole}, 2.
{Polar whale} (Zo["o]l.), the right whale, or bowhead. See
{Whale}.
Coordinate \Co*["o]r"di*nate\, n.
1. A thing of the same rank with another thing; one two or
more persons or things of equal rank, authority, or
importance.
It has neither co["o]rdinate nor analogon; it is
absolutely one. --Coleridge.
2. pl. (Math.) Lines, or other elements of reference, by
means of which the position of any point, as of a curve,
is defined with respect to certain fixed lines, or planes,
called co["o]rdinate axes and co["o]rdinate planes. See
{Abscissa}.
Note: Co["o]rdinates are of several kinds, consisting in some
of the different cases, of the following elements,
namely:
(a) (Geom. of Two Dimensions) The abscissa and ordinate of
any point, taken together; as the abscissa PY and
ordinate PX of the point P (Fig. 2, referred to the
co["o]rdinate axes AY and AX.
(b) Any radius vector PA (Fig. 1), together with its angle
of inclination to a fixed line, APX, by which any
point A in the same plane is referred to that fixed
line, and a fixed point in it, called the pole, P.
(c) (Geom. of Three Dimensions) Any three lines, or
distances, PB, PC, PD (Fig. 3), taken parallel to
three co["o]rdinate axes, AX, AY, AZ, and measured
from the corresponding co["o]rdinate fixed planes,
YAZ, XAZ, XAY, to any point in space, P, whose
position is thereby determined with respect to these
planes and axes.
(d) A radius vector, the angle which it makes with a fixed
plane, and the angle which its projection on the plane
makes with a fixed line line in the plane, by which
means any point in space at the free extremity of the
radius vector is referred to that fixed plane and
fixed line, and a fixed point in that line, the pole
of the radius vector.
{Cartesian co["o]rdinates}. See under {Cartesian}.
{Geographical co["o]rdinates}, the latitude and longitude of
a place, by which its relative situation on the globe is
known. The height of the above the sea level constitutes a
third co["o]rdinate.
{Polar co["o]rdinates}, co["o]rdinates made up of a radius
vector and its angle of inclination to another line, or a
line and plane; as those defined in
(b) and
(d) above.
{Rectangular co["o]rdinates}, co["o]rdinates the axes of
which intersect at right angles.
{Rectilinear co["o]rdinates}, co["o]rdinates made up of right
lines. Those defined in
(a) and
(c) above are called also {Cartesian co["o]rdinates}.
{Trigonometrical co["o]rdinates} or {Spherical
co["o]rdinates}, elements of reference, by means of which the
position of a point on the surface of a sphere may be
determined with respect to two great circles of the
sphere.
{Trilinear co["o]rdinates}, co["o]rdinates of a point in a
plane, consisting of the three ratios which the three
distances of the point from three fixed lines have one to
another.
polar coordinates
polar coordinates in ...
polar coordinates robot
polar corpuscle
polar covalence
polar covalent bond
polar crane
polar crystal
polar curve
polar cushion
polar cushion of glom...
polar cusp
polar cyclone
polar dab
polar day
polar decomposition
polar developable
polar diagram
polar diagram recorder
polar dial
polar diameter
polar disc
polar displacement
polar distance
polar distribution
polar divisor
polar duplex
polar dye
polar easterlies
polar easterlies index
polar echo
polar effect
polar electrojet
polar element
polar elementary storm
polar equation
polar excitation
polar excitation law
polar expedition ship
polar expedition vessel
polar explosive
polar face
polar factorization o...
polar fibers
polar figure
polar filament
polar finder
polar flagella
polar flattening
polar fluid
polar form
Polar form of complex...
polar formula
polar front
polar furrow
polar fusion nucleus
polar geography
polar geology
polar geomorphology
polar glacier
polar coordinates in ...
polar coordinates robot
polar corpuscle
polar covalence
polar covalent bond
polar crane
polar crystal
polar curve
polar cushion
polar cushion of glom...
polar cusp
polar cyclone
polar dab
polar day
polar decomposition
polar developable
polar diagram
polar diagram recorder
polar dial
polar diameter
polar disc
polar displacement
polar distance
polar distribution
polar divisor
polar duplex
polar dye
polar easterlies
polar easterlies index
polar echo
polar effect
polar electrojet
polar element
polar elementary storm
polar equation
polar excitation
polar excitation law
polar expedition ship
polar expedition vessel
polar explosive
polar face
polar factorization o...
polar fibers
polar figure
polar filament
polar finder
polar flagella
polar flattening
polar fluid
polar form
Polar form of complex...
polar formula
polar front
polar furrow
polar fusion nucleus
polar geography
polar geology
polar geomorphology
polar glacier

 英德
英德 有道
有道 百度
百度 谷歌
谷歌 图片
图片 维基
维基 百科
百科